Window 10 Enterprise : Manual Activating
To Launch Command Prompt as Administrator:
1. Click the Windows 10 Start Menu (hitting the Windows key on the keyboard if not already there).
2. Type cmd on the keyboard which will bring up the Windows 10 search.
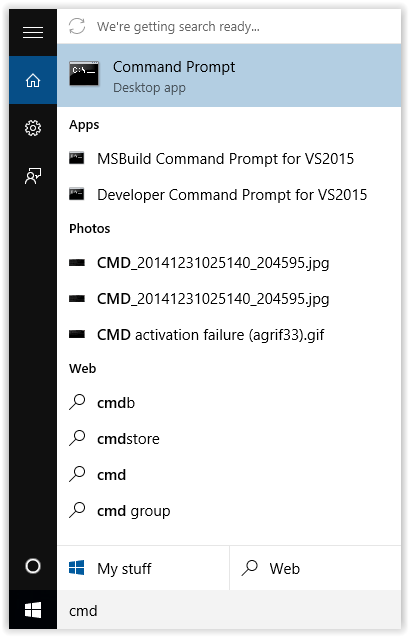
3. Right-click on the Command Prompt app.

4. Click the Run as administrator button at the top of the screen.

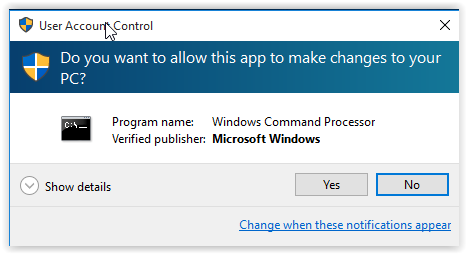
5. Click Yes if the Windows 10 UAC prompt is displayed.
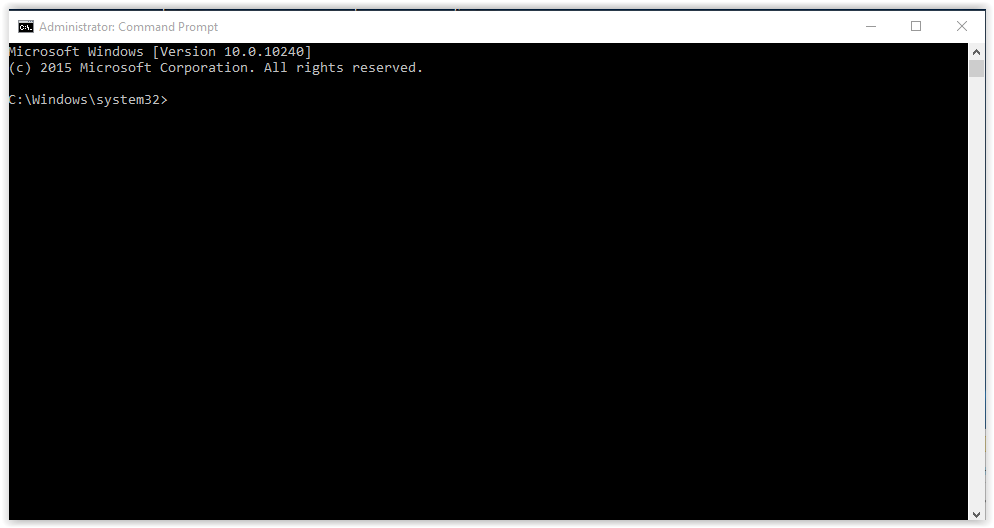
6. The Windows Prompt screen should now open.
Windows 10 Enterprise: Manually Activating
1. Click the Windows 10 Start Menu (hitting the Windows key on the keyboard if not already there).
2. Type cmd on the keyboard which will bring up the Windows 10 search.

3. Right-click on the Command Prompt app.

4. Click the Run as administrator button at the top of the screen.

5. Click Yes if the Windows 10 UAC prompt is displayed.

6. The Windows Prompt screen should now open.

1. Type in “cd \windows\system32” then Press Enter. (Only necessary if the command is not already in the Command Prompt.)
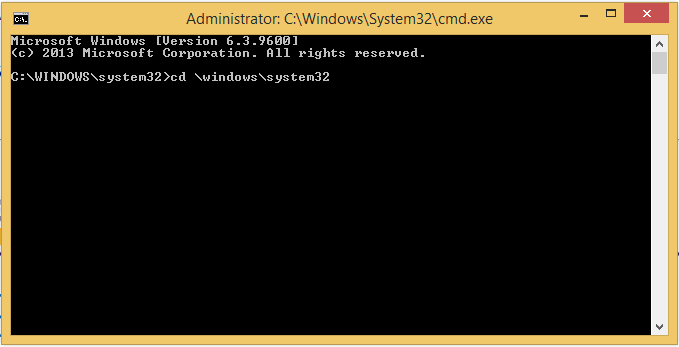
2. Type the cscript command (below) then press Enter: (This should be done directly after "cd \windows\system32>". If this is not in the prompt,)
- cscript \windows\system32\slmgr.vbs /ato
(Please type in the command exactly as shown above, including the spaces.)
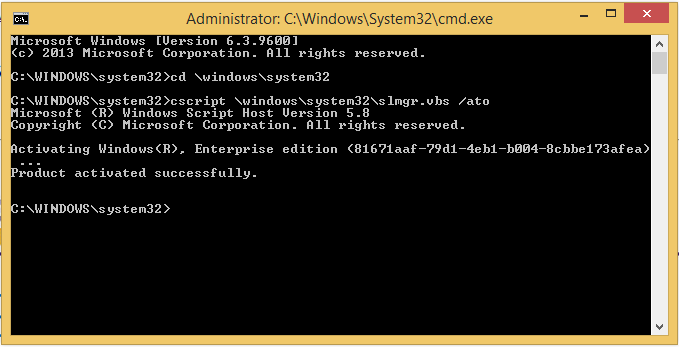
3. How to interpret the Output Message:
- If the Output Message IS Product activated successfully:
- The Product Activation Is Complete!
- The Product Activation Is Complete!
- If the Output Message IS NOT Product activated successfully:
- Make a Note of the Error Code or Output Message.
- Use this document to resolve Common Error Codes:
Important Notes
Completing these steps outlined above WILL Activate your Microsoft Product for the time period as required in the Software License Agreement between LSU & Microsoft.
Microsoft Requirements:
- Windows 10 Enterprise REQUIRES Reactivation EVERY 180 Days.
- Re-activation can occur AUTOMATICALLY and does when:
- Your Computer is Connected to LSU Wi-Fi (Eduroam)
- or - - Your Computer is Connected to the LSU VPN
- Your Computer is Connected to LSU Wi-Fi (Eduroam)







